VoIP 101
You see it in business articles and advertisements everywhere – VoIP. But what is it? VoIP stands for Voice over Internet Protocol. Put simply, VoIP is a technology to send voice calls over the internet, similar to how computers send and receive files over the internet.
In order to understand the capabilities of VoIP, it’s helpful to know a bit about how it works. Essentially, the audio of a phone call gets digitized into data “packets” by microprocessors that are built in to IP telephones and other VoIP-supporting devices. These data packets are then transmitted real-time over your Local Area Network (LAN), across your Wide Area Network (WAN) connection, to your carrier, and finally to your caller.
These simple network maps illustrate the difference between a traditional configuration and one using VoIP.
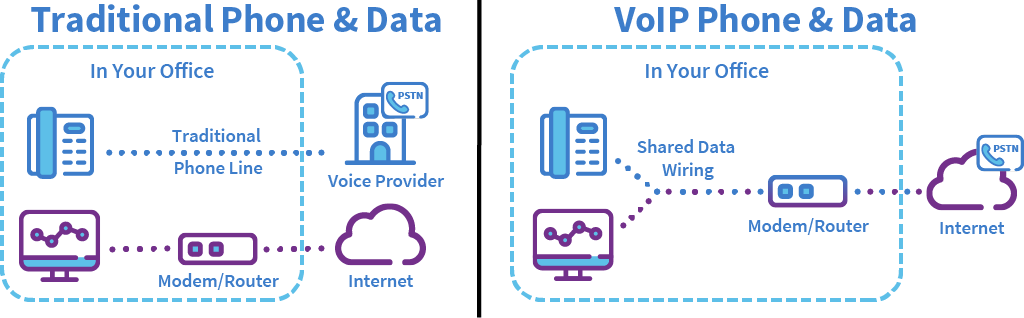
There are a number of reasons that businesses are moving to Voice over IP solutions. VoIP allows computers and phones to use the same LAN cabling in your office, which greatly reduces the costs involved in maintaining separate voice and data networks. Also, due to its internet-based nature, VoIP opens the door to a host of productivity features that tie together phone calls, Instant Messaging, faxes and voicemail, even video conferencing. Collectively, these features are commonly referred to as Unified Communications.
Some people may still think that VoIP is synonymous with poor reliability and voice quality. This is likely due to past experiences with poorly executed VoIP implementations. Early on, companies were offered VoIP with the promise of cutting costs. And while the result was often cheaper, poor implementations also resulted in poor audio quality and dropped calls, which translated to lost productivity and tarnished image. As with any new technology, VoIP had its growing pains.
Voice over IP is now a mature and proven technology that works much better given today’s improvements in internet bandwidth. VoIP is absolutely capable of delivering excellent reliability and voice quality, so long as the proper measures are put in place. Since VoIP calls will travel over both your LAN and WAN, let’s take a closer look at reliability and voice quality through the lens of both of these segments:
- Your LAN
- Reliability. Your LAN connects all of the computers, printers, IP phones, and mobile devices in your office, using either a wired or wireless (WiFi) connection. Therefore, the equipment that comprises your LAN – including cabling, Ethernet switches, firewalls, and wireless access points – all must be properly configured and of sufficient quality. Furthermore, many of today’s business-grade firewalls can be configured to support automatic failover when using a dual connection configuration, a high-reliability solution we’ll discuss more in a moment.
- Voice Quality. As we saw in the illustration above, the VoIP packets must compete against other data packets that may be trying to come or go over your LAN and WAN at the same time; packets such as large file downloads, cloud application usage, and streaming video. Any delays in when those VoIP packets arrive at their destination will result in degraded audio. However, your LAN can be made to prioritize which packets may use your WAN connection first, by way of a network setting known as Quality of Service (QoS). QoS is configurable in many modern firewalls and managed Ethernet switches, and full service providers may even offer installation and configuration of such devices to support their VoIP solutions.
- Your WAN
- Reliability. The WAN connection is responsible for transmitting VoIP calls from the LAN to the VoIP carrier. Since VoIP allows for both internet and voice traffic to use the same WAN connection, many providers recommend a single connection configuration. While a single WAN connection may seem tempting as a cost reducing measure, this configuration is a step backwards in reliability. If that one connection has an issue, both internet and voice are affected! You’ll need to carefully consider options to reduce that risk, such as a dual WAN connection configuration with automatic failover. Ideally, the connections would be provided by different carriers for the added benefit of diversity. This setup utilizes two different WAN connections connected to a firewall that is configured to realize when one connection fails and automatically shift traffic to the other carrier’s connection. Sound complex? Don’t worry – a full service VoIP provider will be able to take care of this for you.
- Voice Quality. There is a wide range of internet connections available today, varying in bandwidth, reliability, and price. Refer to our Internet Connection Comparison Chart to compare some of the most popular connections and see which are suitable for VoIP. And although it is important to ensure that your WAN connection has the bandwidth it will need to transport your voice and data traffic, VoIP calls actually use a surprisingly small amount of bandwidth. Be sure to check out our article, ‘What’s In Your Internet Pipe?’ for more insights before you spend money increasing your bandwidth. You may find that you are already paying for much more bandwidth than you could ever use!

Voice over IP represents the cornerstone of Unified Communications and the future of internet and telecommunications, however there are important considerations to be made before implementing it. The ideal VoIP configuration to experience all of the benefits and limit risk is automatic failover between two connections from different carriers. Not all VoIP carriers will be able to provide a hybrid implementation like this, but now you have the knowledge needed to ask the right questions before you make a decision.
POPP is proud to provide business VoIP services with Automatic Failover configurations – including SIP Trunks, PRI, and land lines – to small and medium-sized businesses in the Twin Cities of Minneapolis and St. Paul, MN. For more information on Voice over IP and how it can help your business lower its communications costs while increasing productivity, please contact us!
Thank you!